How EPCY works
EPCY is a general method to rank genes (or features) according to their potential as predictive (bio)markers, using quantitative data (like gene expression).
Visual description of the method implemented in EPCY
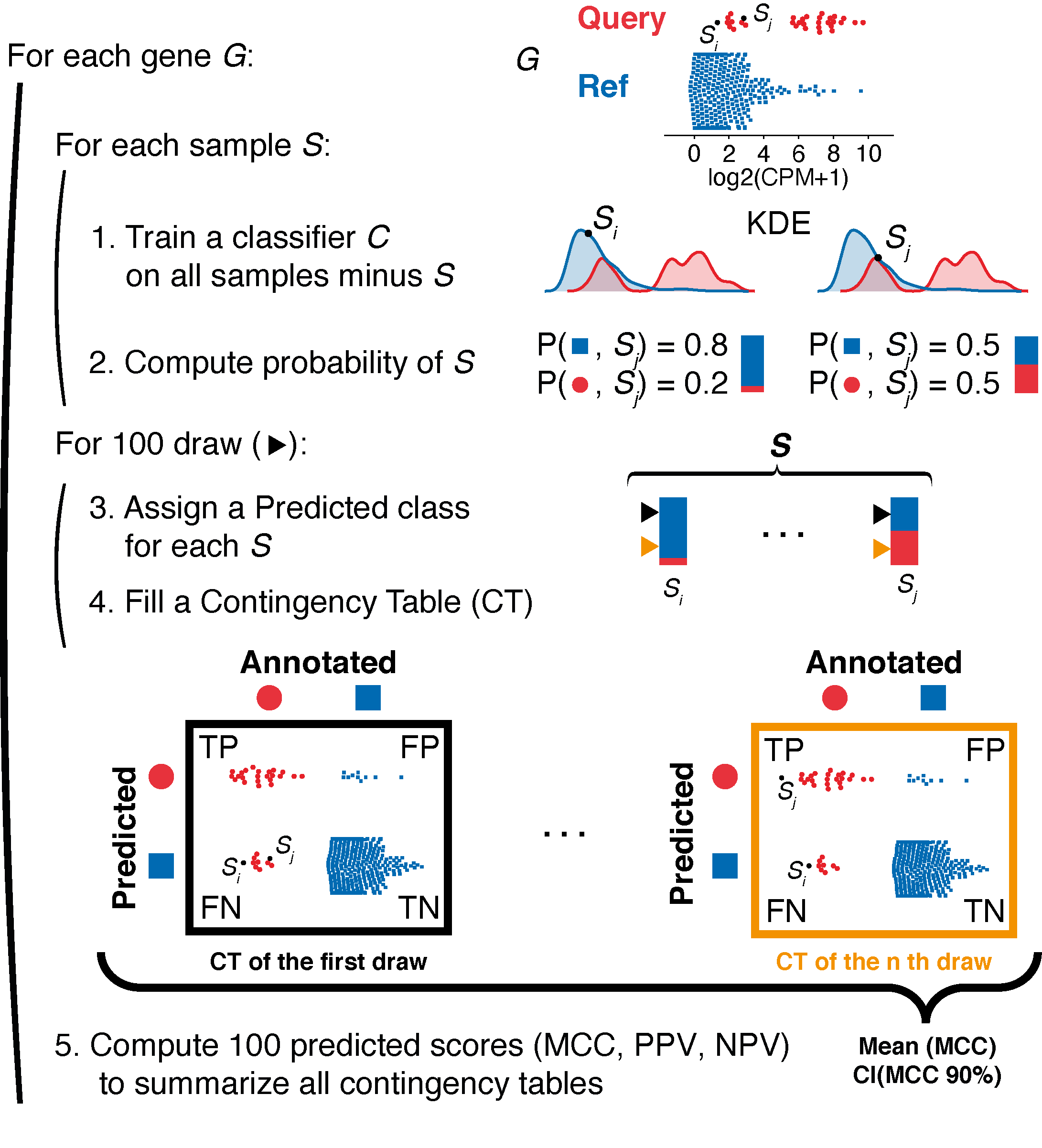
EPCY evaluates each gene’s predictive capacity through a leave-one-out cross-validation protocol. Subgroup densities are first modeled by a Kernel Density Estimation (KDE) and used as part of a classifier Ckde on all samples minus one. Then Ckde is used to compute the probability of each class of the removed sample. This procedure is repeated for each sample. Next, we fill a contingency table (CT) by randomly drawing, for each sample, a predicted class according to the classifier’s probability. This procedure is repeated m times to create m CTs (m = 100 by default). Finally, a Matthew’s correlation coefficient (MCC) is computed for each CT and these values are summarized as a mean MCC with a confidence interval (CI).
EPCY can also reports other predictive scores.