Working on RNA quantification
In contrast to most Differential Expression methods specifically designed to analyse RNA quantification data, EPCY is a generic method that can be used to analyse several types of quantification data, similarly to statistical tests. However, EPCY provides specific tools, pred_rna and profile_rna, to streamline the analysis of RNA data.
bulk RNA
In the First steps with EPCY, we saw how to run EPCY on normalized quantitative data. However, EPCY can work directly on read counts, using pred_rna tool:
# The commande seen in first steps sections
epcy pred --log -t 4 -m cpm.tsv -d design.txt --subgroup AML --query t15_17 -o ./30_t15_17_vs_70/ --randomseed 42
# Equivalent analysis using read counts quantification and pred_rna
epcy pred_rna --cpm --log -t 4 -m readcounts.tsv -d design.txt --subgroup AML --query t15_17 -o ./30_t15_17_vs_70_readcounts/ --randomseed 42
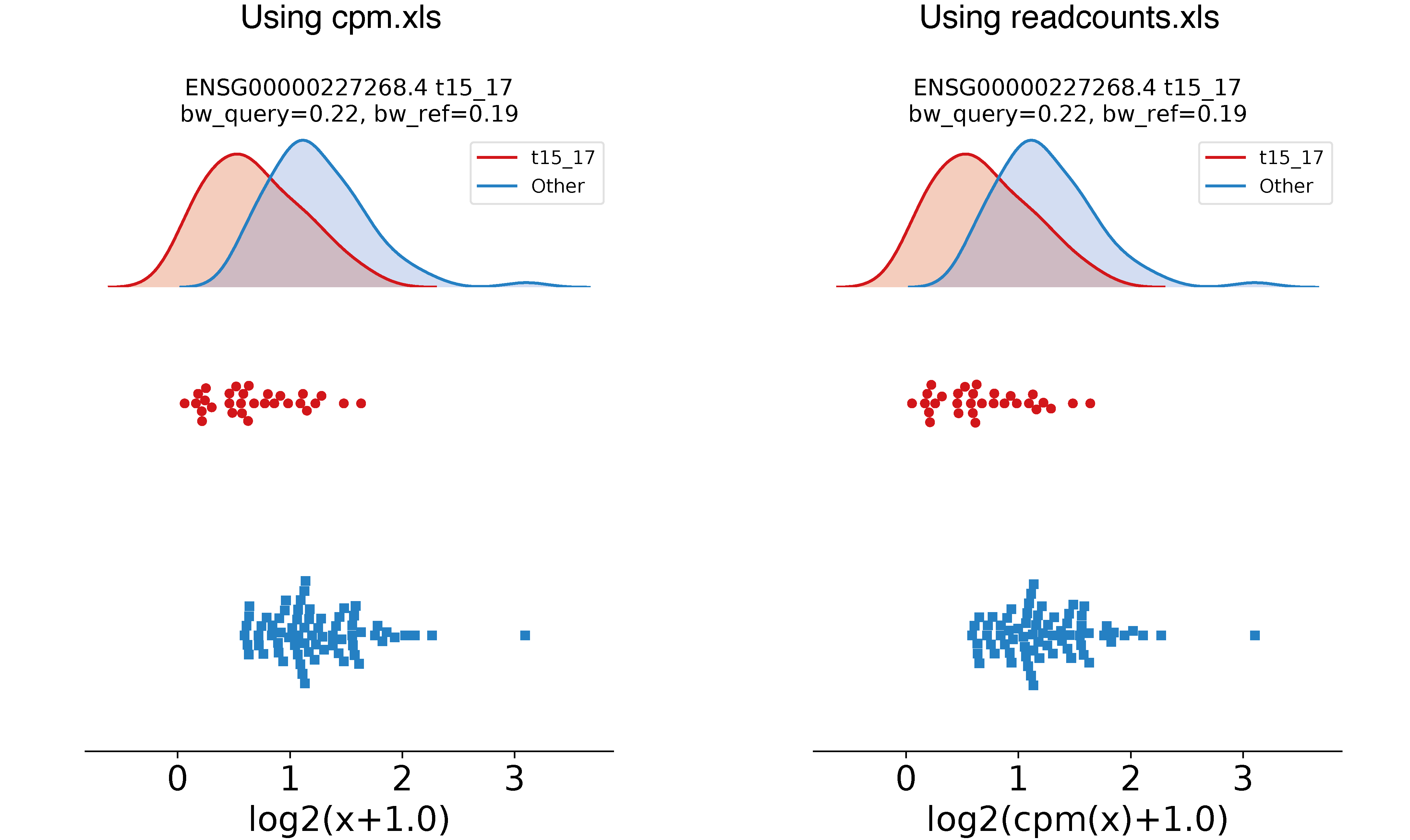
Similarly, you can use profile_rna to plot a trained KDE with its gene expression distribution, directly from read counts:
# The commande seen in first steps sections
epcy profile --log -m cpm.tsv -d design.txt --subgroup AML --query t15_17 -o ./30_t15_17_vs_70/figures/ --ids ENSG00000162493.16 ENSG00000227268.4
# Equivalent commande using read counts and profile_rna
epcy profile_rna --cpm --log -m readcounts.tsv -d design.txt --subgroup AML --query t15_17 -o ./30_t15_17_vs_70_readcounts/figures/ --ids ENSG00000162493.16 ENSG00000227268.4
More help can be found using:
epcy pred_rna -h
epcy profile_rna -h
Kallisto quantification
EPCY allows to work directly on kallisto [1] transcript quantifications using the HDF5 files to take into consideration the expression values of bootsrapped samples computed by this software. To do so, a kallisto column needs to be added to the design file (which specifies the directory path of the abundant.h5 file for each sample).
Using data available on git and epcy pred_rna, you can run EPCY as follow:
# To run on kallisto quantification, add --kall --cpm --log
epcy pred_rna --kal --cpm --log -d ./data/small_leucegene/5_inv16_vs_5/design.tsv -o ./data/small_leucegene/5_inv16_vs_5/trans/
# Note that:
# - kallisto quantification is on transcript, not on gene
# - On real (complet) dataset, it is recommended to add some threads (-t)
To analyse gene level expression, a gff3 file of the genome annotation needs to be specified, to provide the correspondence between transcript and gene ids. For the Leucegene toy dataset, which was quantified using Ensembl annotatiosn, this file can be downloaded from ensembl and added in the command, as follow:
# To run on kallisto quantification and gene level, add --gene --anno [file.gff]
epcy pred_rna --kal --cpm --log --gene --anno ./data/small_genome/Homo_sapiens.GRCh38.84.reduce.gff3 -d ./data/small_leucegene/5_inv16_vs_5/design.tsv -o ./data/small_leucegene/5_inv16_vs_5/gene/ --randomseed 42
epcy profile_rna --kal --cpm --log --gene --anno ./data/small_genome/Homo_sapiens.GRCh38.84.reduce.gff3 -d ./data/small_leucegene/5_inv16_vs_5/design.tsv -o ./data/small_leucegene/5_inv16_vs_5/gene/figures --ids ENSG00000100345
# If you prefer analyse your data on tpm, replace --cpm by --tpm
To take account the inferential variance (introduced by sleuth [2]), EPCY can use bootstrapped samples, using --bs:
epcy pred_rna --kal --cpm --log --gene --bs 10 --anno ./data/small_genome/Homo_sapiens.GRCh38.84.reduce.gff3 -d ./data/small_leucegene/5_inv16_vs_5/design.tsv -o ./data/small_leucegene/5_inv16_vs_5_bs/gene/ --randomseed 42
epcy profile_rna --kal --cpm --log --gene --bs 10 --anno ./data/small_genome/Homo_sapiens.GRCh38.84.reduce.gff3 -d ./data/small_leucegene/5_inv16_vs_5/design.tsv -o ./data/small_leucegene/5_inv16_vs_5_bs/gene/figures --ids ENSG00000100345
When reading all kallisto files is time consuming, you can use epcy kal2mat tool, to create a quantification matrix file and use EPCY, as before:
# Without bootstrapped samples
epcy kal2mat --gene --anno ./data/small_genome/Homo_sapiens.GRCh38.84.reduce.gff3 -d ./data/small_leucegene/5_inv16_vs_5/design.tsv -o ./data/small_leucegene/5_inv16_vs_5_mat/gene/
epcy pred_rna --cpm --log -d ./data/small_leucegene/5_inv16_vs_5/design.tsv -m ./data/small_leucegene/5_inv16_vs_5_mat/gene/readcounts.tsv -o ./data/small_leucegene/5_inv16_vs_5_mat/gene/ --randomseed 42
epcy profile_rna --cpm --log -m ./data/small_leucegene/5_inv16_vs_5_mat/gene/readcounts.tsv -d ./data/small_leucegene/5_inv16_vs_5/design.tsv -o ./data/small_leucegene/5_inv16_vs_5_mat/gene/figures --ids ENSG00000100345
# With bootstrapped samples
epcy kal2mat --gene --bs 10 --anno ./data/small_genome/Homo_sapiens.GRCh38.84.reduce.gff3 -d ./data/small_leucegene/5_inv16_vs_5/design.tsv -o ./data/small_leucegene/5_inv16_vs_5_mat_bs/gene/
epcy pred_rna --bs 10 --cpm --log -d ./data/small_leucegene/5_inv16_vs_5/design.tsv -m ./data/small_leucegene/5_inv16_vs_5_mat_bs/gene/readcounts.tsv -o ./data/small_leucegene/5_inv16_vs_5_mat_bs/gene/ --randomseed 42
epcy profile_rna --bs 10 --cpm --log -m ./data/small_leucegene/5_inv16_vs_5_mat_bs/gene/readcounts.tsv -d ./data/small_leucegene/5_inv16_vs_5/design.tsv -o ./data/small_leucegene/5_inv16_vs_5_mat_bs/gene/figures --ids ENSG00000100345
Single-cell
Several developments are planned in order to facilitate the use of EPCY for single-cell data (to manage sparse matrix and run on GPU for instance). In the meantime, you can analyse your single-cell data with epcy pred and epcy profile using the RNA-seq pipeline described in First steps with EPCY on normalized expression data.
On read counts (not normalized), you can use epcy pred_rna and epcy profile_rna with --cpmed (in place of --cpm) to normalized read counts according to median depth of the dataset.
epcy pred_rna --cpmed --log ...